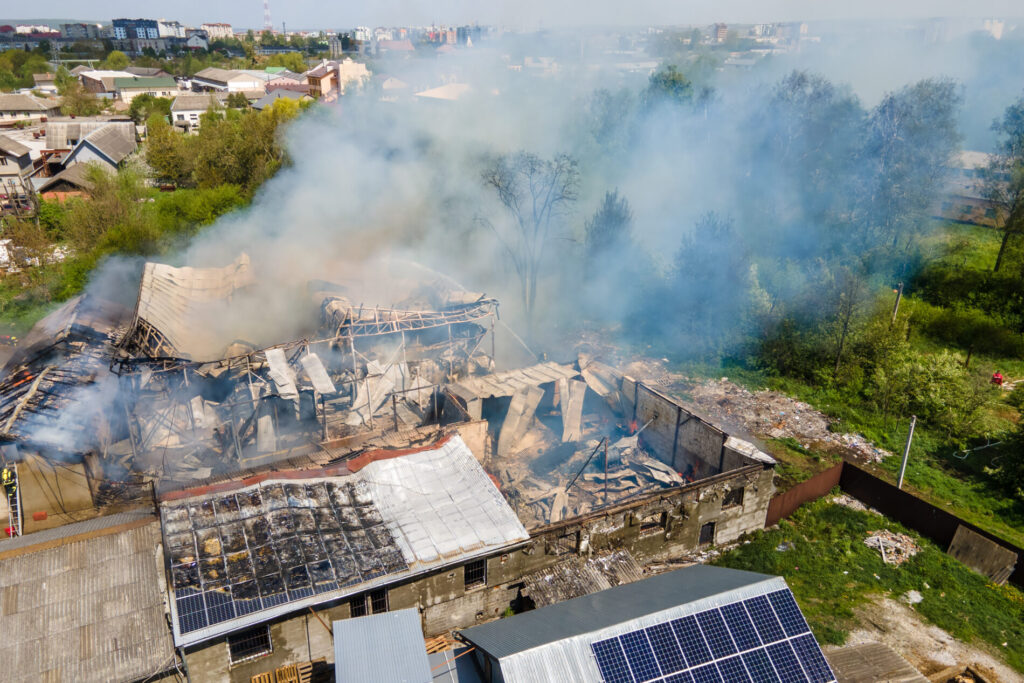
When fine particulates interact with air and an ignition source, the result can be catastrophic. Beyond causing extensive damage to infrastructure, industrial explosions pose severe threats to worker safety and environmental health. Implementing preventative measures and adhering to safety standards is essential for ensuring operational continuity and reducing potential liabilities.
How Explosions Occur
Explosion risks in industrial environments often stem from a combination of combustible materials, oxygen, and an ignition source—a trio sometimes referred to as the “Explosion Triangle.” Dust, when dispersed into the air in the right concentrations, can create a volatile atmosphere. Fine particles of materials like flour, sugar, wood dust, or industrial powders are surprisingly flammable. When ignited by electrical sparks, overheated equipment, or friction, these airborne particles can trigger a chain reaction.
Understanding the science behind explosions is the first step toward effective prevention. A significant factor is the Minimum Explosible Concentration (MEC), which varies across substances. For an explosion to occur, the dust concentration in the air must exceed this threshold. Additionally, factors such as particle size, humidity, and containment geometry can influence the severity of an explosion.
Standards and Regulations for Explosion Mitigation

Due to the devastating impact of industrial explosions, regulatory agencies worldwide have developed stringent standards to promote safety. Key standards in the U.S. include those established by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), with guidelines like NFPA 654 (Standard for the Prevention of Fire and Dust Explosions) serving as a critical reference. Internationally, the ATEX Directives in Europe outline similar requirements for explosive atmospheres, ensuring a standardized approach to equipment design and facility safety.
Adhering to these standards is vital not just for compliance but also for reducing risk. The NFPA emphasizes measures such as risk assessments, explosion protection systems, and proper ventilation. Periodic inspections and employee training are also requirements, ensuring that workers understand proper handling techniques and emergency procedures.
Preventative Measures for Explosion Risks
Preventing explosions begins with identifying problem areas within the facility. Conducting a dust hazard analysis (DHA) is an essential step for determining where combustible dust is likely to accumulate and how it could ignite. This process evaluates equipment like conveyors, mixers, and storage bins and identifies areas for improvement.
One effective method of mitigation is controlling fugitive dust—loose particles that often escape during material handling processes. Modern solutions, such as dust-tight components, play a crucial role in limiting particle dispersion. These components not only seal completely to prevent leaks but also enhance overall safety by minimizing potential ignition opportunities.
For facilities already managing substantial dust volumes, explosion vents and suppression systems provide an added layer of protection. Explosion vents are designed to direct any released pressure away from critical equipment and personnel, while suppression systems detect rising pressure early and release chemicals to neutralize an ignition.
The Role of Advanced Equipment in Explosion Mitigation
Investing in high-quality, engineered equipment is pivotal in mitigating explosion risks. Vortex Global, for example, offers a range of dust-tight equipment options specifically designed for challenging industrial operations. These components reduce the likelihood of dust escape, limiting the conditions necessary for an explosion.
Unlike conventional designs, modern dust-tight solutions are engineered with safety at their core, incorporating features like dust tight seals, robust construction, and wear-resistant materials. Such features ensure reliable performance under the extreme conditions often found in industries like agriculture, cement, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing.
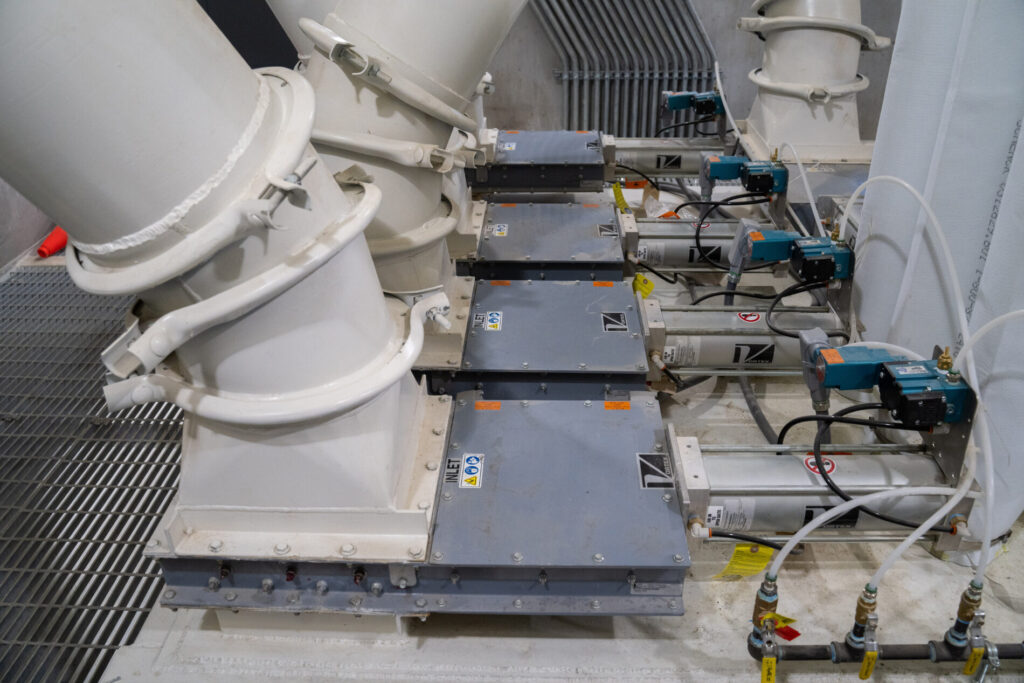

Additionally, incorporating automated systems increases operational safety. Automated valves with position sensors and real-time monitoring features can instantly detect irregularities and promptly shut down operations to prevent escalation. These advancements not only improve safety but also enhance operational efficiency by reducing downtime.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
The repercussions of an explosion extend far beyond physical infrastructure. Failing to adequately manage explosion risks can have significant environmental consequences, such as the release of harmful chemicals into the air or water. Additionally, it can lead to lasting reputational damage and strained relations with local communities.
By addressing explosion risks proactively, industrial companies align themselves with ethical, safety-first principles, demonstrating a commitment to their workers, the public, and the environment. Preventing explosions also minimizes financial losses, including costly fines, legal fees, and insurance premiums.
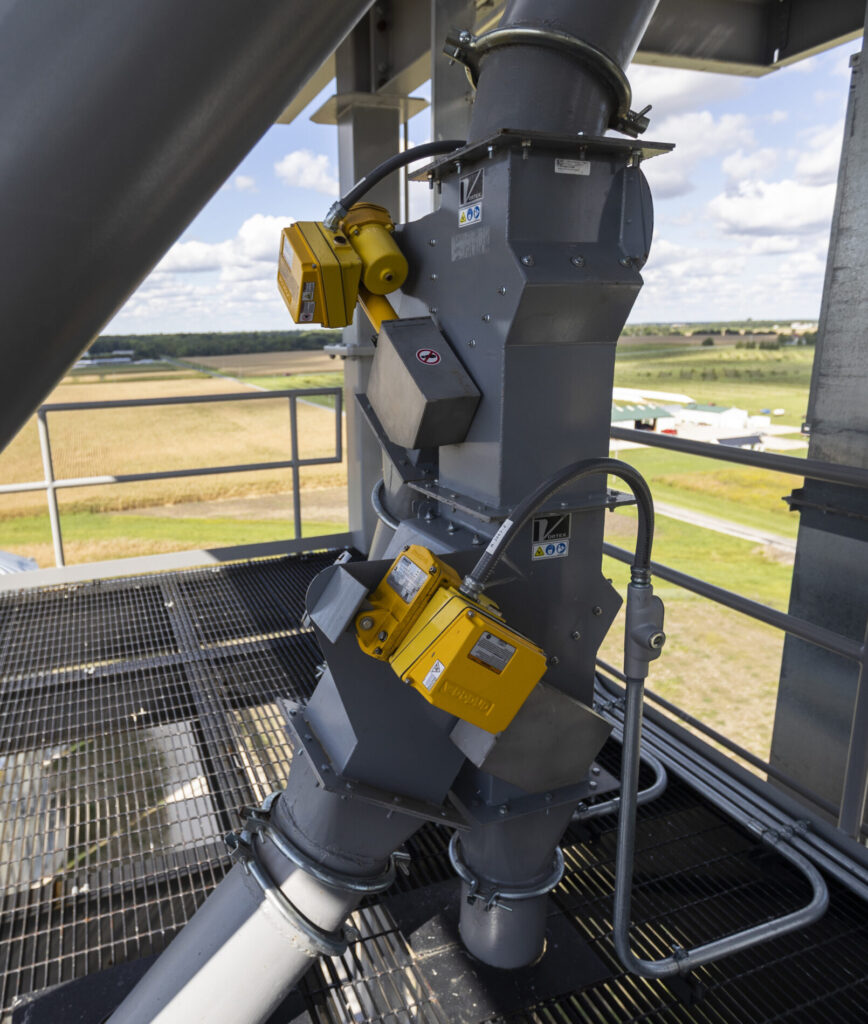

A Proactive Stance on Safety
Mitigating explosion risks requires a multifaceted approach, combining strict regulatory adherence, advanced equipment, continuous monitoring, and a culture of safety throughout the organization. Collaborating with a reputable equipment provider enhances efforts to reduce risks effectively.
Whether you’re planning a new facility or upgrading an existing one, taking proactive steps to prevent explosions is a critical investment in your operations. Don’t leave safety to chance. By implementing modern dust-tight solutions and adhering to recognized safety standards, you protect not just your infrastructure, but also your employees and the environment.