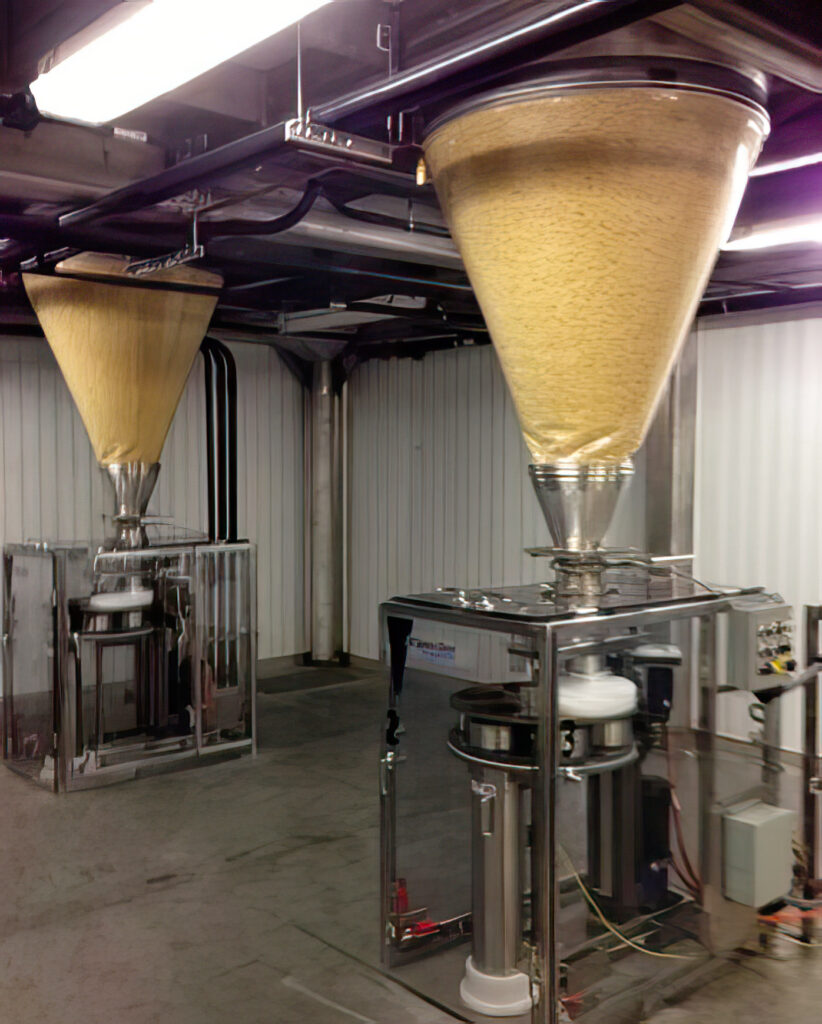
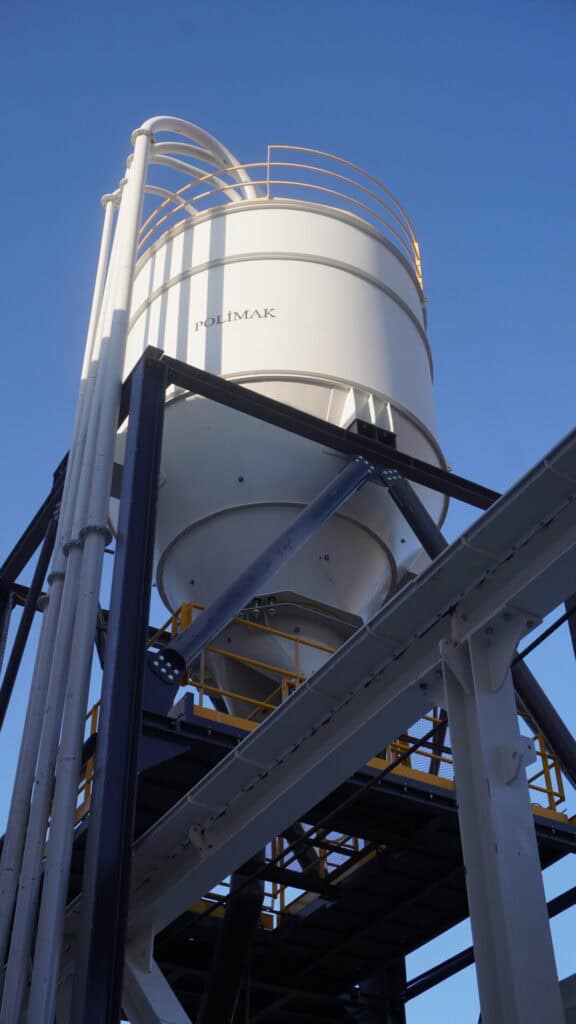
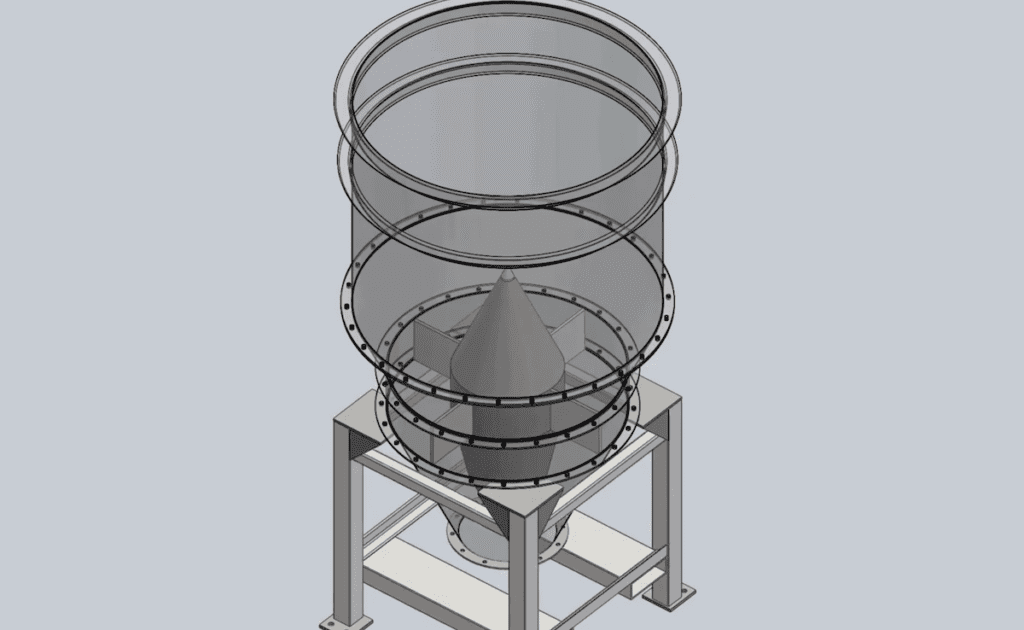
Silos are large structures that are used to separate and store different types of bulk materials, such as grain, coal, cement, carbon, and more different bulk goods. It generally consists of a vertical cylinder and a sloping. Three types of silos are in widespread use today: tower silos, bunker silos, and bag silos.
Tower silos are cylindrical structures, typically 30 to 275 ft (10 to 90 m) in height. They can be made of many materials, such as wood staves, concrete staves, cast concrete, and steel panels. An advantage of tower silos is that the silage tends to pack well due to its own weight, except in the top few feet.
Bunker silos are trenches, commonly with concrete walls, that are filled and packed with tractors and loaders. The filled trench is covered with a plastic tarp to make it airtight. These silos are usually unloaded with a tractor and loader.
Bag silos are heavy plastic tubes, usually around 8 to 12 ft (2.4 to 3.6 m) in diameter, and of variable length as required for the amount of material to be stored. They are packed using a machine made for the purpose and sealed on both ends.