Understanding Powder Sieving
What is Powder Sieving?
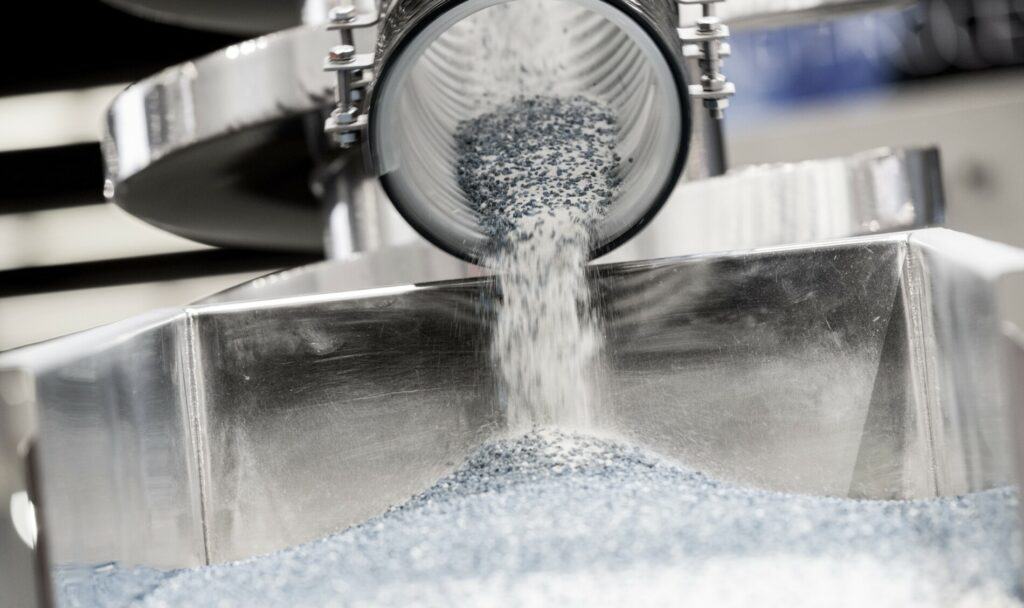
Powder sieving stands as a fundamental technique for controlling particle size distribution. This process involves the passage of powder through a sieve featuring predefined openings, effectively segregating particles based on size. By sieving, manufacturers can eliminate oversized or undersized particles, ensuring a more uniform distribution and enhancing product consistency and quality.
The Significance of Sieving in Particle Size Control
Sieving plays a crucial role in achieving powders’ desired particle size distribution. It eliminates oversized particles that could compromise product quality and consistency, ensuring uniform processing and end-product characteristics. Moreover, sieving enhances dissolution rates, crucial in pharmaceutical applications where rapid and complete dissolution is essential for effective drug delivery.
Optimizing Sieve Selection
Effective sieve selection is paramount for ensuring uniformity and consistency in end products. Understanding particle size requirements and material characteristics is fundamental in this process. Manufacturers can optimize sieve performance and achieve the desired particle size distribution by considering factors such as particle shape, sieve material, and aperture size.
Methods of Controlling Particle Size
Particle size control can be achieved through various methods, including mechanical techniques, chemical methods, thermal processes, comminution, and classification. Each method offers unique advantages and is selected based on the application’s specific requirements.
Mechanical milling breaks down particles through shear forces, with parameters like milling time and speed adjusted for desired PSD. Crystallization relies on factors such as temperature and agitation to control particle nucleation and growth. Spray drying adjusts feed concentration and drying conditions to achieve the desired particle size.
Chemical methods like precipitation or emulsion polymerization manipulate reaction parameters to control particle size during synthesis. Advanced techniques such as nanoparticle fabrication offer precise control over particle size at the nanoscale.
Characterization techniques like laser diffraction and microscopy analyze PSD, aiding in process refinement and ensuring product consistency.
In summary, achieving optimal particle size distribution involves a mix of methods and techniques, allowing industries to enhance product quality and efficiency.
Insights for Engineers
Engineers across all industrial markets must grasp the intricacies of particle size distribution and the role of powder sieving in optimizing it. By incorporating the following insights into their practices, they can enhance product quality and streamline manufacturing processes:
Comprehensive Understanding of Particle Size Requirements: Engineers should thoroughly comprehend a given application’s desired particle size distribution. This understanding forms the basis for selecting appropriate sieves and optimizing sieve performance.
Material Characteristics Evaluation: Assessing the physical and chemical properties of the powder is crucial for effective sieve selection. Factors such as particle shape, density, and moisture content influence the sieving process and must be considered.
Optimization of Sieve Parameters: Engineers should meticulously consider sieve parameters such as mesh size, sieve material, and design features to achieve optimal particle size distribution. Experimentation and data analysis can aid in fine-tuning these parameters for enhanced performance.
Integration with Particle Size Control Techniques: Powder sieving should be integrated with other particle size control methods to maximize effectiveness. Engineers should explore complementary techniques such as comminution or classification to efficiently achieve desired particle size distributions.
Continuous Improvement through Monitoring and Analysis: Implementing robust monitoring and analysis mechanisms allows engineers to optimize powder sieving processes continuously. Regular product quality and performance evaluation enables proactive adjustments to enhance efficiency and consistency. In conclusion, powder sieving is crucial in particle size control, ensuring product quality and industry performance. By understanding the significance of sieving and optimizing sieve selection, manufacturers can achieve the desired particle size distribution and enhance the quality of their products.
Key Takeaways
- Particle size control techniques influence product quality and performance across industries.
- Powder sieving is a fundamental technique for achieving powders’ desired particle size distribution.
- Effective sieve selection ensures uniformity and consistency in end products.
- Understanding particle size requirements is fundamental for optimizing sieve performance.
- Powder sieving remains critical in ensuring product quality amidst evolving industrial landscapes.
By adhering to these principles and leveraging advancements in powder handling technology, engineers can drive innovation and excellence in particle size control, ultimately delivering superior products to consumers worldwide.