Moisture measurement technologies and benefits
Moisture levels present in raw materials and finished products play a critical role in manufacturing quality and consistency. They also have a bearing on costs – water weight is heavy and manufacturers can lose millions of dollars when moisture levels are too high. Those buying and shipping out materials with too much water weight are shouldering needless costs.
There are several available methods for moisture measurement in industrial manufacturing settings, including visual inspection; manual testing; oven weight loss; and moisture sensors. Manufacturers who rely on simple “guesstimates” based on sight or feel determined in a visual inspection cannot provide the necessary consistency or quality. Conducting manual testing by taking samples and bringing them to a laboratory for analysis adds considerable time to the entire process chain. Another possibility is the traditional oven weight loss moisture method, also known as the drying oven method or loss-on-drying (LOD) method. This method measures the moisture content of a sample by weighing it before and after heating it in an oven.[1] While useful, this technique may end up burning off more than just moisture; it can burn off protein inside food or melt PVC inside a pellet.
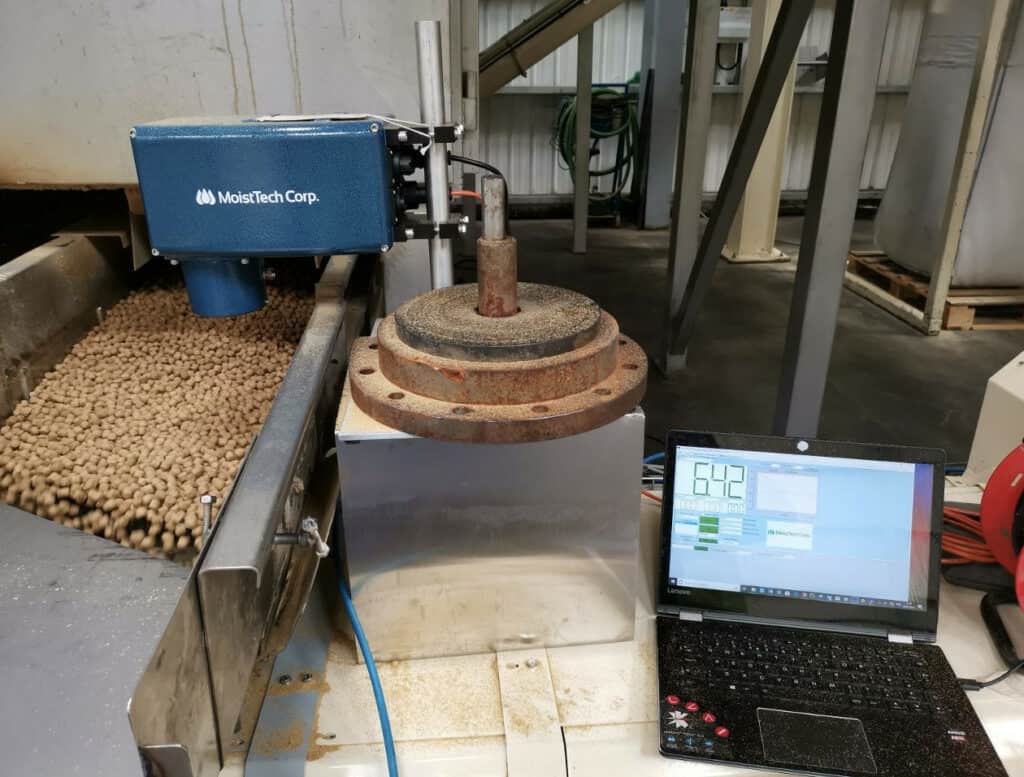
A more robust technology is the use of moisture sensors. One example is MoistTech’s moisture sensor technology, a non-destructive method of measuring and controlling moisture content. Based on near-infrared (NIR) technology that enables moisture measurement without coming into contact with the product, the moisture sensing technology avoids wasted products, gives instant, accurate, and repeatable results, and uses a simple light source for measurement, allowing for longer use of equipment. The sensors have been used on a wide variety of applications, including adhesives, chemicals, coating, converting, food, forest products, hemp/cannabis, minerals, paper, plastics, renewable energy, textiles, tobacco, and web.