Understanding Combustible Dust in Dairy Processing
Combustible dust refers to fine particles generated during material processing that can combust under certain conditions when suspended in the air. This dust primarily arises in dairy processing from milk powder, whey powder, and other powdered dairy products during manufacturing, conveying, and packaging processes. When dispersed in the air, these powders create a potentially explosive atmosphere if ignited.
Risks and Hazards
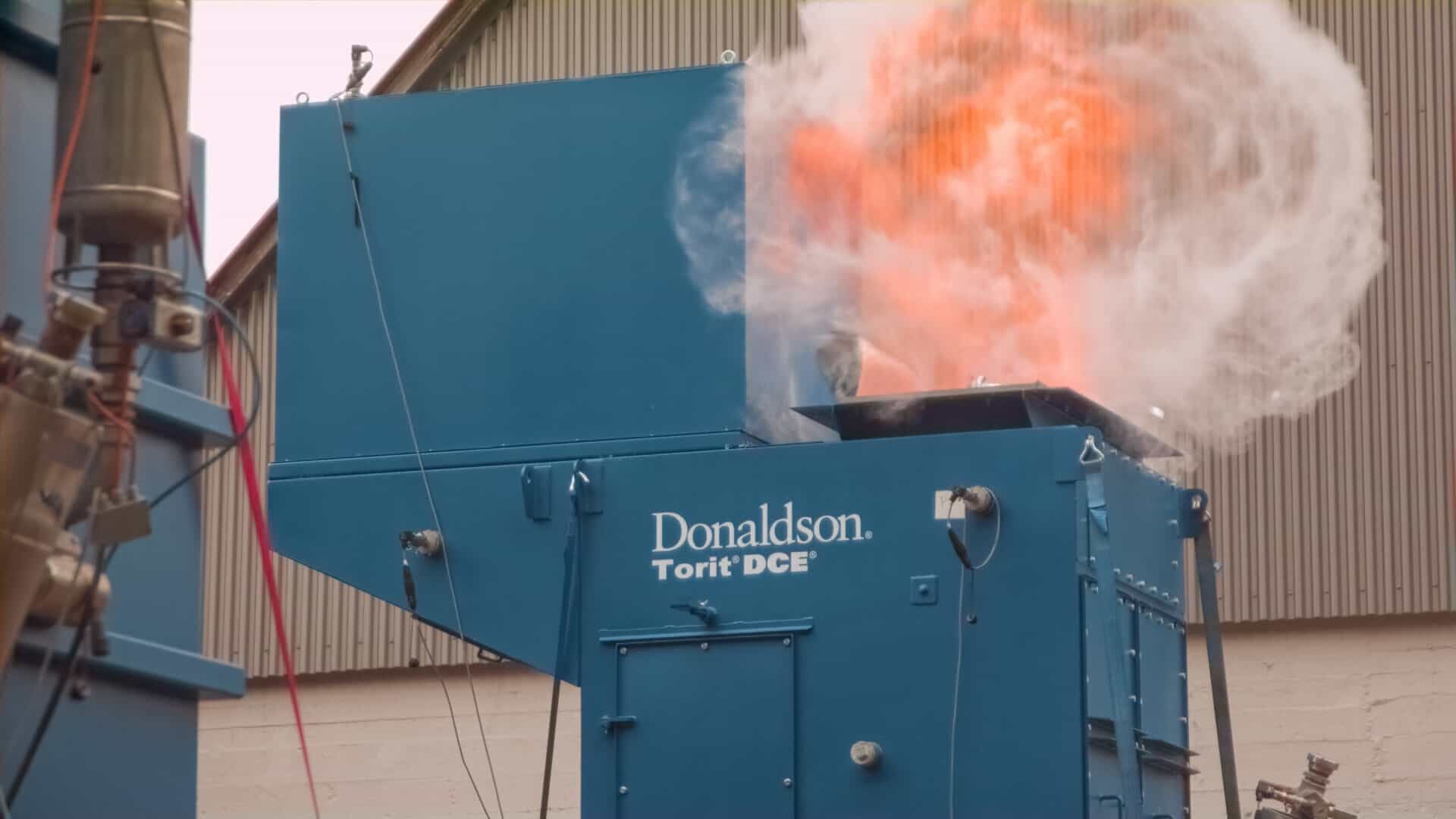
The dangers associated with combustible dust in dairy processing are significant. These particles can trigger explosions when ignited, leading to devastating consequences such as structural damage, injuries, loss of life, and production downtime. Furthermore, the dairy industry’s hygiene standards mean that equipment and surfaces often have residual dust, exacerbating the risk.
Factors Contributing to Combustible Dust Explosions
Several factors contribute to the risk of combustible dust explosions in dairy processing facilities:
- Particle Size and Composition: Finer particles with larger surface areas are more prone to combustion. Being fine and organic, dairy powders can easily ignite when dispersed in the air.
- Oxygen Presence: Combustible dust requires oxygen to ignite. Dust particles can accumulate in confined spaces or poorly ventilated areas, creating an explosive atmosphere when combined with air.
- Ignition Sources: Sparks from machinery, static electricity, open flames, or hot surfaces can ignite suspended dust particles.
Preventative Measures and Safety Protocols
To mitigate the risks associated with combustible dust in dairy processing, implementing robust safety measures and protocols is imperative:
- Risk Assessment and Hazard Identification: Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify areas prone to dust accumulation and potential ignition sources.
- Engineering Controls: Employ engineering solutions like proper ventilation systems, dust collection equipment, and explosion protection devices to minimize dust dispersion and contain potential explosions.
- Housekeeping and Maintenance: Regular cleaning and maintenance schedules help minimize dust accumulation on surfaces and equipment.
- Training and Education: Educate workers about combustible dust risks, safe handling procedures, and emergency response protocols.
- Compliance with Standards: Adhere to regulatory standards such as NFPA 652 and NFPA 654, which provide guidelines for managing combustible dust hazards.
Conclusion
The risks associated with combustible dust in dairy processing facilities demand a proactive and comprehensive approach to safety. By understanding the sources and risks and implementing stringent preventive measures, the industry can safeguard its workforce, assets, and reputation. Regular risk assessments, adherence to safety standards, adequate ventilation, and continuous training are pivotal in mitigating the potentially devastating consequences of combustible dust explosions.
In essence, prioritizing safety, fostering a culture of awareness, and investing in preventive measures are crucial steps in ensuring a secure environment within dairy processing facilities, ultimately safeguarding lives and maintaining operational continuity.