The types of bulk feeders
There are two basic types of bulk feeders used in bulk solids industrial plants name: volumetric feeders and gravimetric feeders.
Volumetric feeders
As the name suggests, volumetric feeders modulate and control the bulk material’s discharging volumetric flow rate (m3/s or ft3/s). They are simply dosing systems that supply bulk material to a system or unit with a specific volume at specific time intervals. Some common models include screw feeders, rotary feeders also known as rotary valves, belt feeders, and vibrating pans.
Gravimetric feeders.
These feeders modulate the dry material’s mass flow rate (kg/s or lb/s) which can either be done on a continuous basis or batch basis. The former is concerned with the regulation of material mass discharge per unit time and the latter involves feeder shut off after the discharge of a specific material mass. The amount of discharged material is measured by weighing devices such as load cells. The common gravimetric feeding methods are gain-in-weight (GIW) and loss-in-weight (LIW).
Types of Bulk Solids Feeders
There are many types of bulk feeders, this includes the following: screw feeders, rotary feeders (rotary valves), belt feeders, apron belt feeders, vibrating pan feeders etc.
Screw feeders
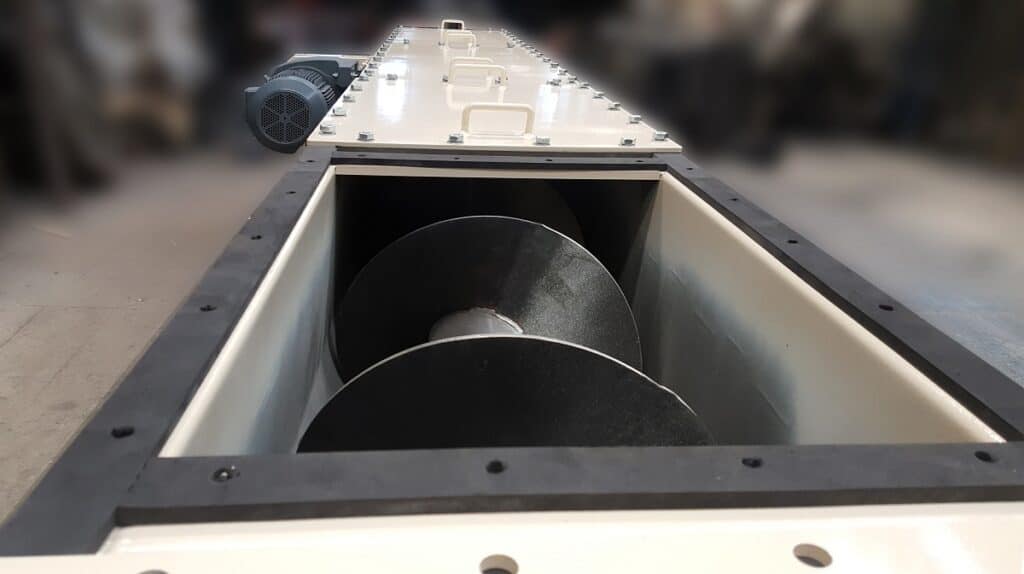
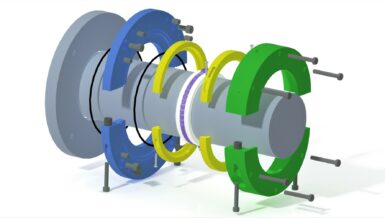
Screw feeders are appropriate for a wide range of bulk materials in granular or powder form in comparison to belt feeders. They are used to mechanically transport bulk materials. A screw feeder is commonly placed at the beginning of the process line and is installed directly to a hopper, a silo or a bin. The screw is enclosed in a housing (tubular or U-shaped volume). The housing has an inlet port attached to the upstream equipment and the outlet port where the material exits is installed to a downstream equipment. During operation, the material is supplied to the equipment via the inlet port. A drive motor turns the screw, moving the material one pitch per revolution. The material is transported along the longitudinal direction of the screw housing until the discharging point (outlet port). From the outlet, the material is fed to the downstream unit or system by the turning screw. The feeder can be installed at a horizontal or inclined position.
There are different models of screw feeders and the common ones utilise single helicoidal screw shafts. Some of the different models Polimak produces are tubular screw feeders, U-type screw feeders, dosing screw feeders, micro-dosing screw feeders, and custom-designed screw feeders. Screw feeders are utilised in some of the following industries; agriculture, chemical, cement, and lime, foundry, paper etc. They are used in many industrial applications such as mixing, dosing and batching systems.
Rotary feeders
Depending on the application requirements, rotary feeders have almost the same design as rotary valves. The feeders have vanes that rotate at a suitable rpm to discharge the bulk material into a unit or system. They are capable of precisely discharging and feeding bulk materials in powder or granular form from hoppers or silos. In some applications where pressure differentials are present, such as a pneumatic operating line, the valve is capable of acting as an airlock feeder. This means that it permits material movement while reducing air leakages. The rotary valve’s vanes form a slightly seal against the housing surface; hence, it can reduce air leakages.
Polimak offers an excellent variety of rotary feeders to help its customers with the efficient handling of bulk solid materials. We aim to design and manufacture state-of-the-art rotary feeders aimed at rendering quality performance during bulk material handling. We provide airlock feeders that operate in industries like chemical, foundry, mining, food, foundry, and many others.
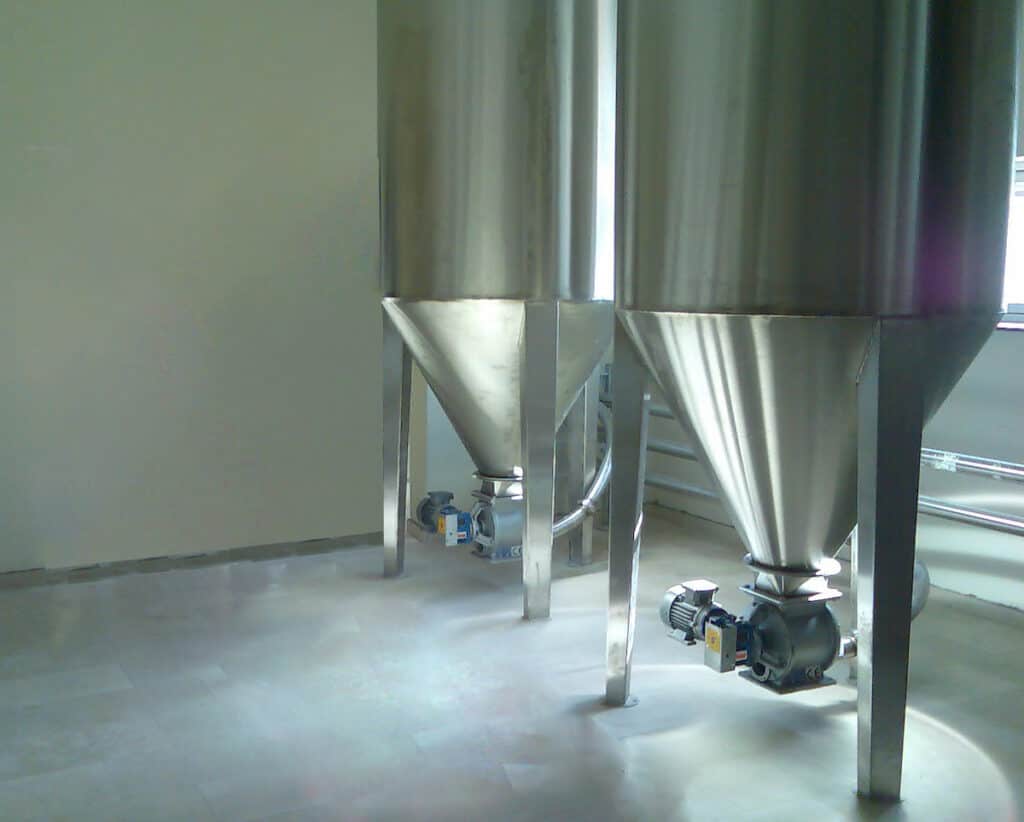

Feeders selection procedure
The bulk solids feeders selection procedure is typically based on several factors which may include temperature, pressure, type of bulk material to be handled, the scope of the feeding rate, the type of upstream equipment, and the type of downstream equipment fed by the feeder. Once these factors are known, the manufacturer can offer help on which bulk feeder would be best for the desired application. Polimak makes sure to guide and render technical help to its customers when it comes to selecting the most optimal bulk feeder for a particular application. Whether the solids feeder type is a volumetric feeder or a gravimetric feeder, it should render at least the following attributes:
- Required amount of bulk material discharge with determined precision and accuracy for a stipulated period.
- Swift, reliable and smooth bulk material flow from the upstream/source equipment.
- Steady bulk material withdrawal from the upstream equipment especially for mass
flow models.
In a measurement context, the terms precision and accuracy are normally used. If a measurement or produce is said to be precise, it simply reflects the reproducibility of the measurements, and if it is accurate, it simply reflects or considers how close a specific measurement is to the acceptable value. In other words, precision is the degree to which a process or system repeats the same measurement, while accuracy is the degree of closeness to the actual measurement. Precision and accuracy are two important aspects in dosing, weighing and batching processes. Having long years of expertise in bulk solids handling industry, Polimak’s engineers provide suitable levels of precision and accuracy for extensive range of applications.
Handled materials
Some of the bulk materials that can be handled with the bulk feeders include cement, calcite, ash, glass powder, marble powder, soybean, sesame, rice, rice flour, dried fruit, nuts, peanut, almond, sunflower seed, cottonseed, grain cereals, chestnut, coffee grain, coffee powder, sugar, salt, spice plastic pellets, sawdust, fly ash, coal, coal dust, wheat, flour, barley, feed, seed, corn, chickpea, bean etc.